Are you tired of feeling stuffy and stale air inside your home? Poor house-ventilation can not only make your living space uncomfortable, but it can also lead to a variety of health issues. From allergies and respiratory problems to the buildup of harmful pollutants, the consequences of inadequate ventilation can be quite serious. However, with a few simple tips, you can easily improve the ventilation in your house and breathe in fresher, cleaner air. Discuss the importance of House Ventilation and provide you with some easy and effective ways to keep the air inside your home fresh and healthy. Say goodbye to stuffy rooms and hello to a more comfortable and inviting living space. Keep reading to find out how you can achieve better house-ventilation.
The Importance of Adequate Ventilation in Modern Homes
In contemporary residences, ensuring that there is sufficient ventilation stands as a crucial component for fostering a salubrious indoor environment. The presence of effective ventilation mechanisms plays a pivotal role in the expulsion of airborne contaminants, which include dust, animal fur, and volatile organic compounds. By facilitating the removal of these pollutants, ventilation systems contribute significantly to the enhancement of air quality within the home.
Moreover, the regulation of humidity levels is another vital function served by adequate ventilation. This is particularly important as it mitigates the risk of mould and mildew formation, scenarios that not only compromise the structural integrity of properties but also pose serious health risks. High humidity levels are known to be conducive to the proliferation of mould spores, which can lead to respiratory issues and exacerbate conditions such as asthma and allergies.
The constant replenishment of stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air is essential in preventing the accumulation of pollutants and in maintaining a healthy living space. This exchange not only purifies the air but also ensures that inhabitants are less likely to suffer from the adverse effects associated with poor air quality. By addressing these concerns, effective ventilation systems thereby contribute to a reduction in the potential for respiratory problems and allergic reactions, underscoring the importance of proper air circulation in modern homes.
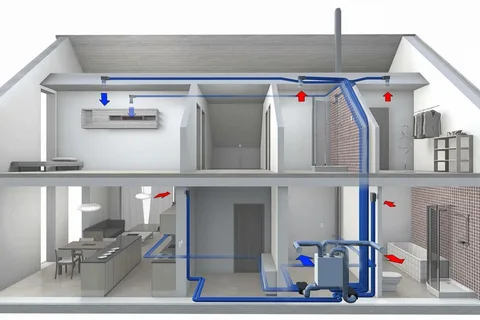
 Understanding the Basics of Heat Exchange System
Understanding the Basics of Heat Exchange System
In the realm of residential architecture, the foundation of a healthy and fresh environment is built upon the effective management of Heat Exchange System. These systems are categorised into two principal types: natural and mechanical ventilation. The former leverages the passive movement of air through spaces, utilising openings such as windows and doors to facilitate the exchange of indoor and outdoor air. This method is largely dependent on the architectural design and the strategic placement of openings to achieve a continuous flow of air, promoting a reduction in the concentration of indoor pollutants without the aid of mechanical devices.
On the other hand, mechanical ventilation systems are engineered to actively control the air flow within a dwelling through the use of fans and air ducts. These systems are designed to offer a more consistent and manageable air quality level, independent of external weather conditions or the natural air flow patterns that influence passive systems. Mechanical ventilation can be particularly advantageous in environments where the external air quality is poor or where specific air quality standards must be rigorously maintained.
Each system presents a series of benefits and limitations that are influenced by a variety of factors, including but not limited to, the climatic conditions of the area, the structural design of the home, and the specific air quality requirements of the occupants. The choice between natural and mechanical ventilation systems, or a hybrid approach incorporating elements of both, requires a careful consideration of these factors to achieve an optimal balance between air quality, energy efficiency, and the overall comfort of the home environment.
Strategies for Natural Ventilation without Compromising Security
In an era where natural ventilation plays an integral role in enhancing indoor air quality without imposing additional energy costs, homeowners seek methods to achieve this balance whilst not undermining the security of their abode. A critical strategy involves the judicious placement of windows and vents, orchestrated to promote cross-ventilation. Such placement ensures a natural flow of air across different sections of the dwelling, facilitating the expulsion of stale air and the admission of fresh air from the outdoors.
Furthermore, the adoption of window screens and security bars is identified as a pragmatic approach. These additions permit air to circulate freely but act as a deterrent against potential intruders, effectively maintaining a home’s security integrity. Moreover, the implementation of ceiling fans emerges as a complementary strategy. These fans do not merely circulate the air within a room; they also enhance the efficiency of cross-ventilation by ensuring a more uniform distribution of air throughout the living spaces.
In addition to these architectural and mechanical adjustments, homeowners are encouraged to consider the temporal aspects of ventilation. Utilising natural ventilation during certain times of the day, especially when external temperatures are more favourable, can significantly augment the effectiveness of these strategies. Such practices not only enhance the indoor air quality but do so in a manner that is congruent with the principles of energy efficiency and environmental stewardship.
Enhancing Passive House Ventilation System with Heat Recovery
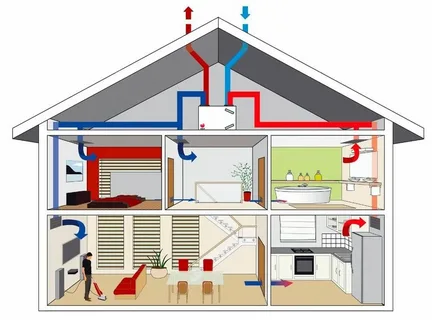
The incorporation of Passive House Ventilation System or Energy Recovery Ventilation (ERV) systems into mechanical ventilation setups presents an innovative approach to enhancing air flow within homes whilst concurrently conserving energy. These systems operate on the principle of transferring heat from the outgoing stale air to the incoming fresh air during the colder months, and vice versa during warmer periods, thereby maintaining a comfortable indoor environment without a significant increase in energy consumption.
HRV and ERV systems are distinguished by their unique capabilities; HRV systems are adept at transferring heat, whilst ERV systems can exchange both heat and moisture, making them particularly beneficial in areas with extreme climatic conditions. The utilisation of these systems facilitates the maintenance of optimal indoor temperatures and humidity levels, contributing to a more pleasant living atmosphere.
By capitalising on the thermal energy present in the exhaust air, these systems reduce the demand on heating and cooling systems, leading to lower energy bills and a reduced carbon footprint for the household. This energy-efficient method of air exchange does not compromise the air quality within the home, ensuring that residents enjoy a fresh and comfortable environment.
The Role of Plants in Improving Indoor Air Quality
Incorporating plants into home décor extends beyond aesthetic appeal, serving a pivotal role in enhancing the air quality within living spaces. Research has underscored the capacity of certain flora, such as spider plants (Chlorophytum comosum) and peace lilies (Spathiphyllum), to not only embellish interiors but also to purify the air. These species stand out for their remarkable ability to absorb pollutants, including benzene, formaldehyde, and trichloroethylene, thus contributing to a reduction in airborne contaminants.
Moreover, the process of photosynthesis allows these plants to take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen, thereby enriching the indoor atmosphere with higher oxygen levels. This exchange plays an essential part in creating a healthier environment for occupants, potentially mitigating the risks associated with poor air quality, such as respiratory issues and cognitive impairment.
It is also worth noting that the presence of greenery indoors can enhance humidity levels through the natural process of transpiration. This is particularly beneficial in environments where dry air is a concern, as maintaining adequate humidity can contribute to respiratory system health and overall comfort.
Understanding the Passive House Heat Exchanger
A Passive House heat exchanger plays a pivotal role in the realm of energy-efficient building design, particularly in achieving and maintaining the rigorous standards set by the Passive House Institute. This innovative technology serves as a key component within the building’s ventilation system, facilitating the exchange of heat between incoming and outgoing air streams. The fundamental principle behind its operation lies in the efficient recovery of thermal energy from the exhaust air before it is expelled from the building.
By capturing and transferring this otherwise wasted heat to the incoming fresh air, the heat exchanger helps to temper the ambient temperature of the incoming air. This process significantly reduces the energy demand associated with heating or cooling the indoor environment, thereby promoting substantial energy savings over the long term.
Moreover, the Passive House-heat exchanger contributes significantly to improving indoor air quality by ensuring a continuous supply of fresh, filtered air. This ventilation strategy not only enhances comfort for occupants but also mitigates issues related to humidity and pollutants, creating a healthier living or working environment.
Regular Maintenance Tips for Heat Exchange System for Home
Maintaining an efficient Heat Exchange System for Home is crucial for ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of the mechanism, whilst safeguarding the quality of indoor air. Regular upkeep can prevent the accumulation of pollutants and facilitate a healthier living environment. Here are several maintenance tips for homeowners to consider:
Inspect and Clean Vents and Ducts
Periodically check vents and ductwork for any debris or obstructions that could impede airflow. It is advisable to remove any dust accumulation or foreign objects that have been trapped to ensure a clear passage for air.
Replace Filters Regularly
Air filters play a vital role in capturing dust, pollen, and other airborne particles. To maintain optimal performance, filters should be replaced every three to six months, depending on usage and environmental factors. In households with pets or individuals with allergies, more frequent changes may be beneficial.
Schedule Professional Inspections
While many aspects of ventilation system maintenance can be handled by homeowners, professional inspections are invaluable. Experts can assess the system comprehensively, identifying potential issues before they escalate into major problems. Annual or bi-annual checks are recommended.
Monitor System Performance
Stay vigilant for any signs of decreased efficiency, such as unusual noises, diminished airflow, or increased energy consumption. These indicators can suggest the need for maintenance or repair.
Ensure Proper Ventilation in High-Humidity Areas
As mentioned, certain areas of the home, like kitchens and bathrooms, are prone to high humidity. Ensuring these spaces are adequately ventilated can prevent moisture accumulation and the consequent growth of mould and mildew.
Adherence to these maintenance tips can significantly contribute to the functionality and efficiency of house-ventilation systems. Regular attention not only enhances indoor air quality but also prolongs the lifespan of the ventilation system, offering a dual advantage of health benefits and cost savings.
Ventilation Solutions for High-Humidity Areas
In areas of the home prone to high levels of humidity, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements, the implementation of bespoke ventilation strategies is essential. The accumulation of excess moisture in these areas not only predisposes the environment to mould and mildew growth but also contributes to a general decline in indoor air quality. One of the most effective measures to counteract this issue involves the installation of extractor fans, which actively expel moist air from the interior to the outside, thereby reducing the humidity levels within the space.
The utilisation of extractor fans equipped with timers or humidity sensors represents a further refinement of this approach. These devices enable the automatic activation of the fan when humidity reaches a predetermined threshold, ensuring that ventilation occurs precisely when needed. This not only optimises the effectiveness of moisture control but also enhances energy efficiency by preventing the fan from operating unnecessarily.
In addition to mechanical solutions, the consideration of ventilation during the design phase of a home can significantly mitigate humidity concerns. Strategic placement of windows and vents to encourage natural air flow can complement mechanical systems, providing an additional avenue for moisture control. Moreover, for areas such as basements, where natural light and ventilation are often limited, the integration of dehumidifiers can serve as an auxiliary measure, further aiding in the maintenance of optimal humidity levels and contributing to a healthier indoor environment.
The Future of House Heat Exchanger Technology
The evolution of House Heat Exchanger technology is on a rapid trajectory, propelled by innovations aimed at enhancing efficiency and user convenience. Smart ventilation systems represent a significant leap forward, enabling homeowners to orchestrate their indoor air quality with unprecedented precision. These cutting-edge systems can be manipulated remotely via smartphone applications, a feature that offers the dual benefits of flexibility and ease of use.
Moreover, the integration of sensors and air quality monitors into ventilation systems marks another advance in the sector. These devices deliver real-time insights into the composition of indoor air, equipping individuals with the information necessary to adjust their ventilation settings for optimal air quality. Such technology not only optimises the living environment but also paves the way for a more responsive and adaptive approach to ventilation management.
The focus on innovation extends to the development of systems designed to enhance energy efficiency. Innovations such as heat recovery ventilators underscore the industry’s commitment to reducing energy consumption while maintaining superior air quality. This convergence of technology and sustainability highlights the ongoing transformation in the field of house-ventilation, indicating a future where comfort, health, and environmental stewardship are inextricably linked. As technology continues to advance, it is anticipated that these systems will become increasingly sophisticated, offering solutions that are not only more effective but also more aligned with the principles of sustainable living.
Understanding Heat Exchange Ventilation
Heat exchange ventilation, also known as heat recovery ventilation (HRV) or energy recovery ventilation (ERV) is a sophisticated system designed to optimize energy efficiency and indoor air quality in buildings. This technology operates by transferring heat between incoming and outgoing air streams, thereby reducing the energy required for heating or cooling indoor spaces.
At its core, heat-exchange ventilation works through a network of ducts that simultaneously ventilate and recover thermal energy from exhaust air before it leaves the building. This recovered heat is then transferred to the incoming fresh air, pre-conditioning it to match the indoor temperature. This process not only helps maintain a consistent and comfortable indoor climate but also minimizes energy loss that would typically occur in traditional ventilation systems.
The benefits of heat-exchange ventilation extend beyond energy efficiency. By continuously circulating fresh air into the building while expelling stale air, these systems enhance indoor air quality by removing pollutants, allergens, and excess humidity. This circulation also helps prevent the buildup of indoor contaminants, contributing to a healthier environment for building occupants.
Conclusion
In synthesising the insights provided, it becomes evident that the trajectory towards maintaining an optimally ventilated home encompasses a spectrum of methodologies, from leveraging natural air currents to integrating sophisticated mechanical systems. The dialogue on House Ventilation underscores its paramount importance in safeguarding not only the structural integrity of dwellings but also the health and well-being of their occupants. Innovations in ventilation technology, coupled with traditional practices and the strategic use of flora, illustrate a comprehensive approach to achieving superior indoor air quality.
FAQs
What is the difference between natural and mechanical ventilation?
Natural ventilation utilises the passive flow of air through openings such as windows and doors, capitalising on architectural designs to facilitate air exchange. Mechanical ventilation, conversely, involves the active movement of air via fans and ducts, offering a controlled environment regardless of external conditions.
How often should House Ventilation filters be replaced?
The replacement of House Ventilation filters is contingent upon several factors, including usage and environmental conditions. Generally, it is advisable to replace filters every three to six months. In households with pets or residents with allergies, a more frequent replacement schedule may be beneficial.
Can plants significantly improve indoor air quality?
Certain plants, such as spider plants and peace lilies, possess the capability to absorb pollutants and enhance oxygen levels through the process of photosynthesis. Whilst they contribute to better air quality, they are most effective when used in conjunction with adequate ventilation systems.
Are Heat Recovery Ventilation (HRv) systems worth the investment?
HRV systems offer a sustainable solution for maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures and humidity levels by recycling the energy from exhaust air. They are particularly valuable in climates with extreme weather conditions, providing both energy efficiency and improved air quality.
How can I ensure my home is well-ventilated without compromising security?
Strategies such as the installation of window screens, security bars, and the use of ceiling fans can enhance air circulation whilst maintaining a home’s security. Additionally, the strategic placement of windows and vents to encourage cross-ventilation can significantly improve air flow without sacrificing safety.
| Other Good Articles to Read |
| niche blogs connect |
| blogs 97 |
| Blog Stitution |
| blogs unplugged |
| blogs cotch rouge |
| blog signatr |
| blog sintonias |
| blog zilla |
| consumer forums |
| finance forums |
| g blogs |
| too blog |
| Related Business Listings |
| Contact Directory |
| Local Business Profiles |